Allergic reactions and hypersensitivity disorders have been a challenge for humans for centuries. Recent advancements have improved our understanding of the complex interplay between the immune system, environment, and genetics. This knowledge is leading to the development of new treatment strategies. This blog post summarizes these advancements for researchers and scientists working to understand and combat allergic diseases.
Understanding Allergic Reactions
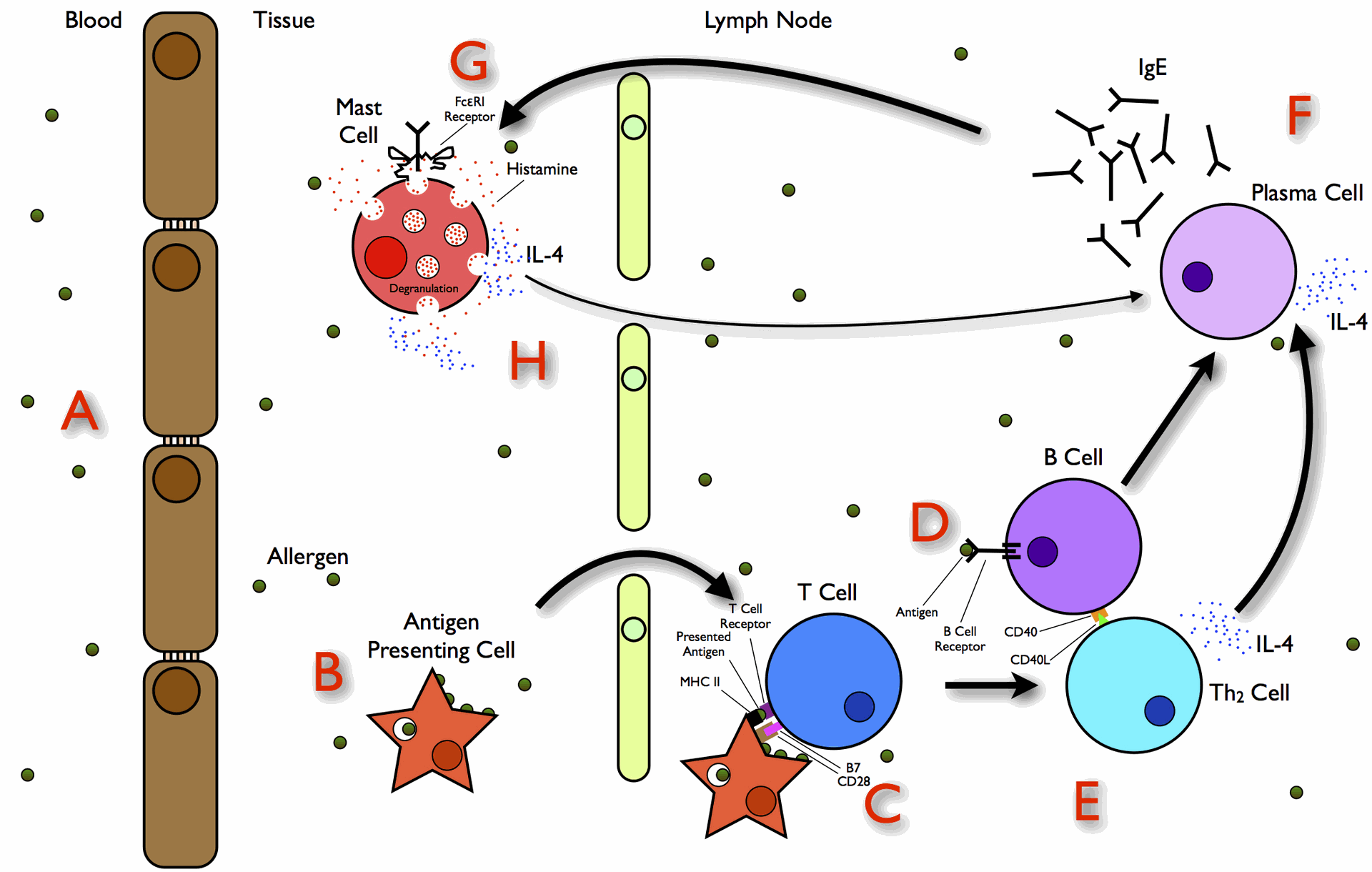
Our understanding of allergic reactions has significantly improved in recent years. We now know that dendritic cells play a critical role. These cells act as sentinels, presenting harmless foreign substances (allergens) to T lymphocytes (immune cells) in an incorrect way. This presentation triggers a Th2-biased immune response. This response involves the release of inflammatory mediators like histamine and IgE (immunoglobulin E). These mediators cause the classic symptoms of allergy, such as runny nose, asthma, and anaphylaxis.
The Environmental Impact
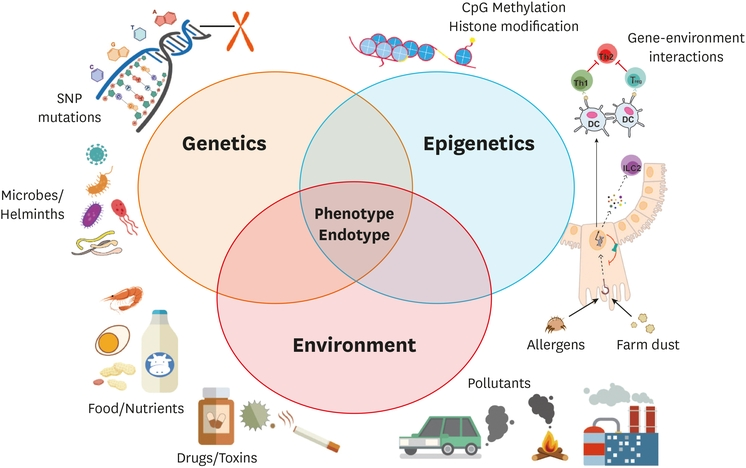
The hygiene hypothesis suggests a link between reduced exposure to microbes in early life and the rise in allergies. Studies show that a balanced gut microbiome is essential for training the immune system and promoting tolerance. Disruption of this balance, potentially caused by overuse of antibiotics or caesarean sections, might contribute to allergic sensitization.
The Role of Genetics
Genetics significantly influences allergy susceptibility. Mutations in genes like filaggrin, which is important for maintaining skin barrier function, have been linked to atopic dermatitis, a risk factor for other allergies. However, genetic predisposition is not absolute. Epigenetic factors, including environmental influences and lifestyle choices, can modify gene expression, potentially reducing or increasing allergic tendencies.
New Treatment Approaches for Allergies and Asthma
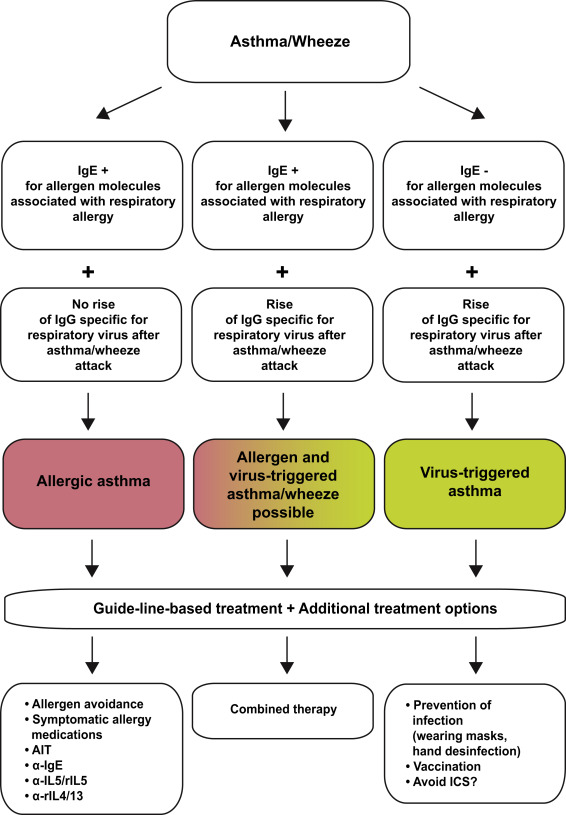
The treatment landscape for allergies and asthma is constantly evolving. Beyond traditional antihistamines and corticosteroids, several promising areas are being explored:
- Immunomodulatory therapies: These drugs aim to regulate the immune response, preventing the overreaction to allergens. Examples include anti-IgE monoclonal antibodies, which target the key mediator of allergic reactions.
- Allergen immunotherapy (AIT): This approach involves gradually increasing allergen exposure to patients to induce tolerance. Sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) tablets offer a convenient and potentially more compliant alternative to traditional allergy shots.
- Microbiome manipulation: Restoring a healthy gut microbiome composition through prebiotics, probiotics, or fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) holds promise for preventing and managing allergic diseases, although more research is needed.
Research Efforts and Reliable Reagents
Research continues to identify new therapeutic targets and treatment strategies. Reliable research reagents are essential for advancing this field. Companies like Gentaur Group, a leading supplier of high-quality immunological reagents, play a critical role in supporting these important investigations.

Conclusion
The field of allergy and hypersensitivity research is making significant progress. With a deeper understanding of the immune mechanisms, environmental impact, and role of genetics, we are closer to developing more effective and targeted therapies. The future holds immense potential for personalized medicine approaches, tailoring treatment strategies to individual patients based on their unique immune profile and genetic makeup.
Allergy and Hypersensitivity: New Insights and Treatment Approaches