Summary: Cancer vaccines aim to trigger the immune system to attack tumors. However, responses vary greatly between patients. Biomarkers are biological indicators that can help predict who will benefit most from cancer vaccines, allowing for more personalized treatment.
Biomarkers for Vaccine Response:
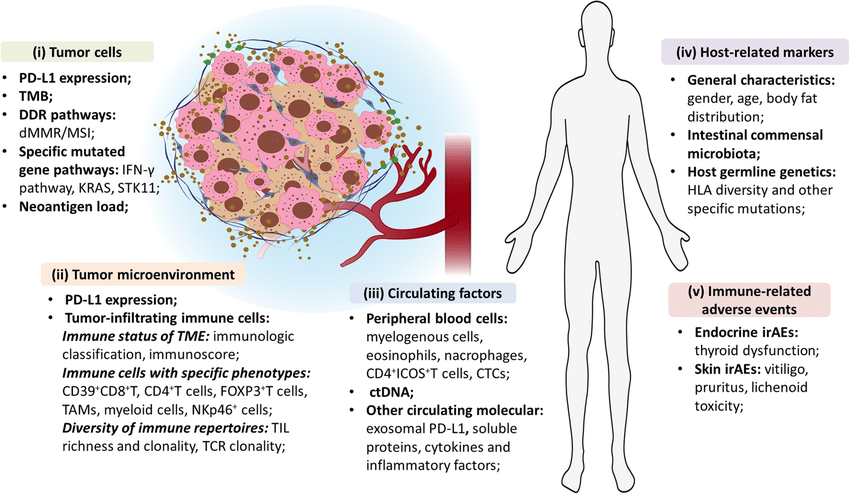
- Tumor characteristics:
- Tumor Mutation Burden (TMB): High TMB indicates more mutations in tumor cells, potentially leading to better response to some therapies like immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and possibly cancer vaccines. This is because more mutations create more neoantigens (unique proteins recognized by the immune system).
- Mismatch Repair (MMR) Deficiency: Tumors with MMR deficiency accumulate mutations faster, increasing TMB and potentially improving response to immunotherapy, including cancer vaccines.
- Immune biomarkers:
- Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs): The presence of TILs within the tumor suggests an existing immune response against the tumor. The number and activation state of TILs, particularly CD8+ T cells, can indicate potential vaccine effectiveness.
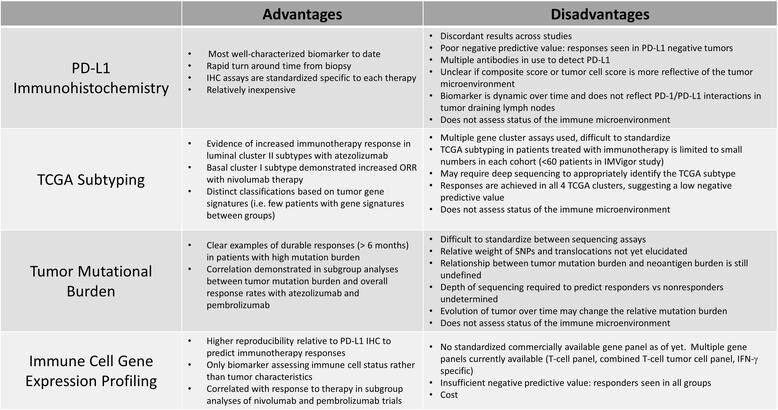
- PD-L1 Expression: PD-L1 is a molecule that suppresses T cell activity and is often elevated in cancer cells. PD-L1 levels can help determine if combining cancer vaccines with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade antibodies might be beneficial to enhance the anti-tumor immune response.
Benefits of Biomarker-Guided Vaccination:
- Personalized therapy: Biomarkers can help select patients for specific cancer vaccines, maximizing treatment effectiveness and reducing side effects in non-responders.
- Clinical trial design: Identifying biomarkers can aid in developing and optimizing cancer vaccines by enrolling patients predicted to respond well.
- Early response monitoring: Regularly monitoring biomarkers during vaccination can provide insights into treatment effectiveness, allowing for adjustments or alternative strategies if needed.
Challenges and Limitations:
- Single biomarker limitations: The complex interplay between tumors and the immune system suggests that one biomarker might not be enough for accurate response prediction. Multi-factorial biomarker panels are likely required for reliable prediction.
- Tumor heterogeneity: Tumors can vary genetically and functionally across different areas and over time. This can lead to discrepancies between biomarker profiles obtained from biopsies and the overall tumor landscape.
- Standardization and validation: Biomarker assays need further standardization and validation across different labs and patient groups to ensure generalizability and clinical usefulness.
Future Directions:
- Multiplex biomarker panels: Research is ongoing to identify and validate panels encompassing multiple biomarkers to comprehensively assess tumor immunogenicity and the patient's immune response. Companies like Gentaur, a supplier of research reagents, are crucial in providing tools and resources for biomarker research.
- Advanced techniques: Integrating advanced technologies like genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics holds promise for uncovering new and more specific biomarkers for vaccine response prediction.
- Liquid biopsies: Developing non-invasive liquid biopsies that analyze biomarkers in blood or other bodily fluids could simplify patient monitoring and overcome limitations associated with tumor biopsies.

Conclusion: Biomarkers are a valuable tool for personalizing cancer immunotherapy with vaccines. By identifying patients most likely to benefit, biomarker-guided vaccination can improve treatment outcomes and advance cancer immunotherapy. However, addressing current limitations through robust biomarker development and validation is essential to fully realize this approach's potential.
Biomarkers in Predicting Response to Cancer Vaccines