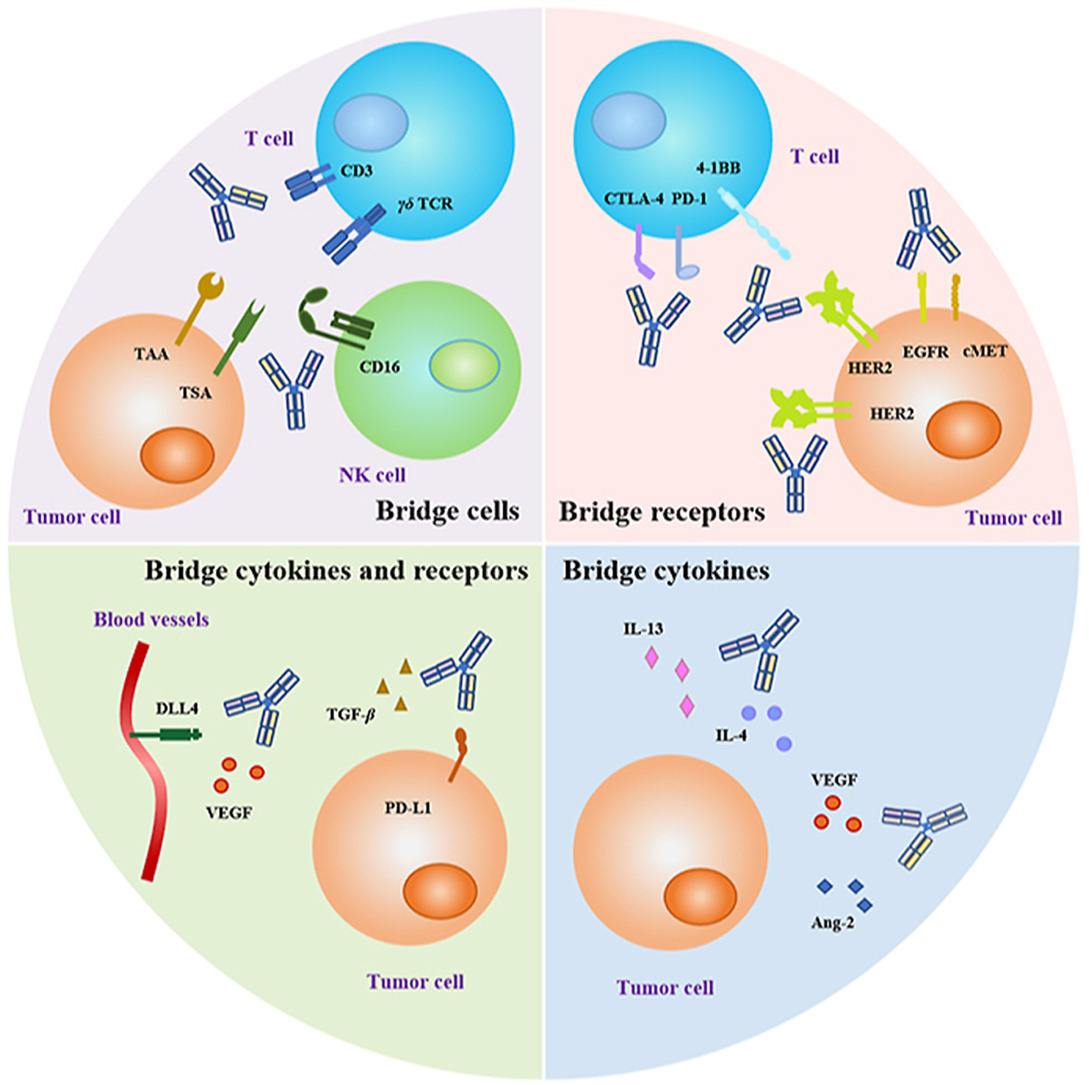
Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) are a promising new class of drugs in cancer immunotherapy. Unlike traditional monoclonal antibodies, BsAbs have two antigen-binding sites. This allows them to target two structures simultaneously:
- One site binds to a specific immune cell, such as a T lymphocyte.
- The other site binds to a tumor-associated antigen (TAA) on the surface of a cancer cell.
By bringing the immune cell and cancer cell into close proximity, BsAbs can activate the immune system to directly attack the cancer cells.
Advantages of BsAbs
- Increased Specificity: BsAbs can target cancer cells more precisely than some existing immunotherapies, potentially reducing side effects.
- Enhanced Immune Activation: BsAbs can directly stimulate immune effector cells, leading to a stronger anti-tumor response.
- Overcoming Immune Escape: BsAbs may target multiple pathways or immune checkpoints, potentially overcoming mechanisms tumors use to evade the immune system.
Clinical Applications and Future Directions
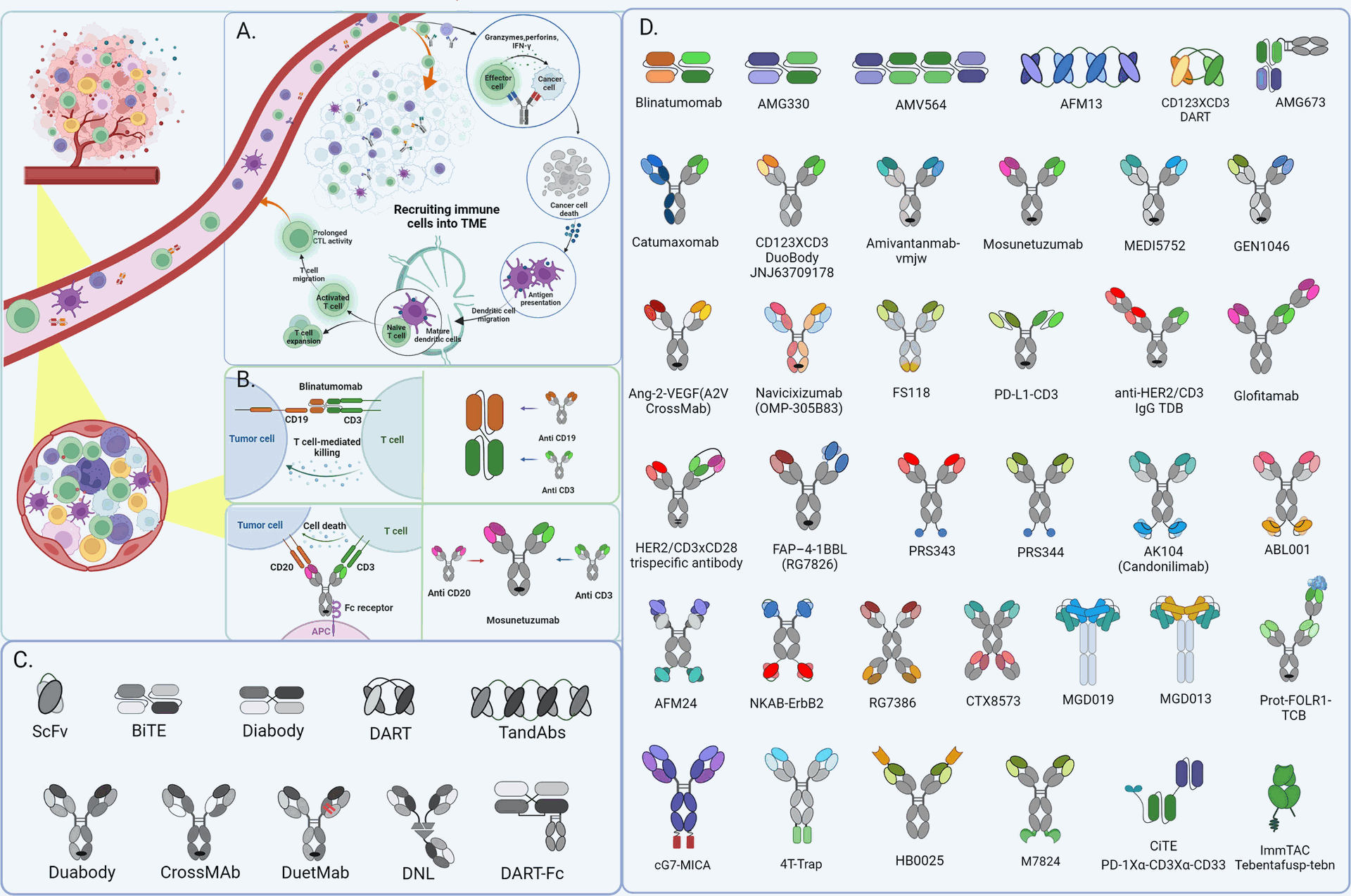
Several BsAbs are being investigated or are already approved for treating various blood cancers and solid tumors. Blinatumomab, for example, is a CD3-CD19 BsAb used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Research is ongoing to explore BsAbs in:
- Combination therapies: Combining BsAbs with other immunotherapies, chemotherapy, or targeted agents for potentially greater effectiveness.
- Targeting new antigens: Identifying and targeting novel cancer-specific antigens or immune checkpoint molecules with BsAbs.
- Improved BsAb design: Engineering BsAbs with better stability, drug delivery, and reduced side effects.
Challenges of BsAbs
Despite their potential, BsAbs come with certain challenges:
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS): Rapid T cell activation by BsAbs can lead to CRS, a serious side effect requiring careful monitoring.
- Manufacturing Complexity: Producing BsAbs can be more complex and expensive than conventional antibodies.
- Target Selection and Validation: Identifying the most effective target antigens and validating their efficacy remains a crucial area of research.
Maxanim: Supporting BsAb Research
Maxanim ( a Gentaur Group Company) , a supplier of research reagents, offers a range of tools to support BsAb research, including highly purified proteins and antibodies for target validation and functional assays.

Conclusion
BsAbs represent a significant advancement in cancer immunotherapy. Their ability to bridge the gap between the immune system and cancer cells offers a unique and powerful therapeutic approach. Continued research focused on optimizing BsAb design, overcoming challenges, and exploring combination therapies has the potential to significantly improve cancer treatment outcomes.
Future Considerations
As BsAb research progresses, several key areas require further investigation:
- Patient selection: Identifying patients most likely to benefit from BsAb therapy based on specific genetic or immunological profiles.
- Next-generation BsAbs: Developing BsAbs with improved functionality, reduced toxicity, and enhanced targeting capabilities.
- Combination strategies: Exploring synergistic effects of BsAbs with other immunotherapies or targeted agents to create personalized treatment regimens.
By addressing these challenges and capitalizing on their unique properties, BsAbs have the potential to revolutionize cancer immunotherapy and significantly improve patient outcomes.
Learn More About Bispecific Antibodies In The Following Video:
Bispecific Antibodies: A New Frontier in Cancer Immunotherapy