The immune system and the nervous system, once viewed as separate entities, are now understood to be intricately connected. This complex interplay influences health and disease in various ways.
The Blood-Brain Barrier: A Selective Gateway
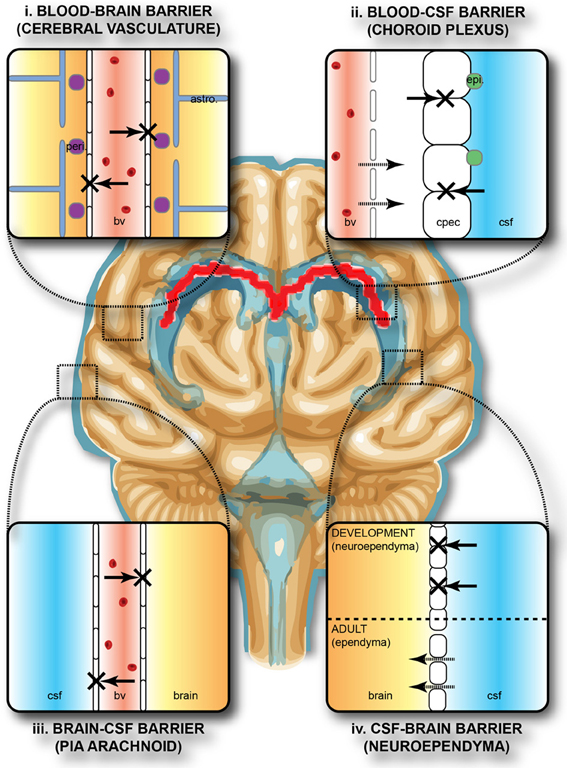
The central nervous system (CNS) is protected by the blood-brain barrier (BBB). This highly selective barrier, formed by specialized endothelial cells with tight junctions, restricts the movement of molecules and immune cells from the bloodstream into the brain. This safeguards the delicate neuronal environment from potentially harmful immune responses.
Immune Guardians Within the CNS
Despite the BBB, the CNS is not entirely devoid of immune activity. Specialized immune cells called microglia and astrocytes reside within the CNS and play a critical role in maintaining tissue health and responding to injury or infection. Microglia act as sentinels, constantly scanning for pathogens and damaged cells. Upon detection of threats, they can activate immune responses or promote repair processes.
Channels of Communication
Communication between the immune and nervous systems occurs through several mechanisms:
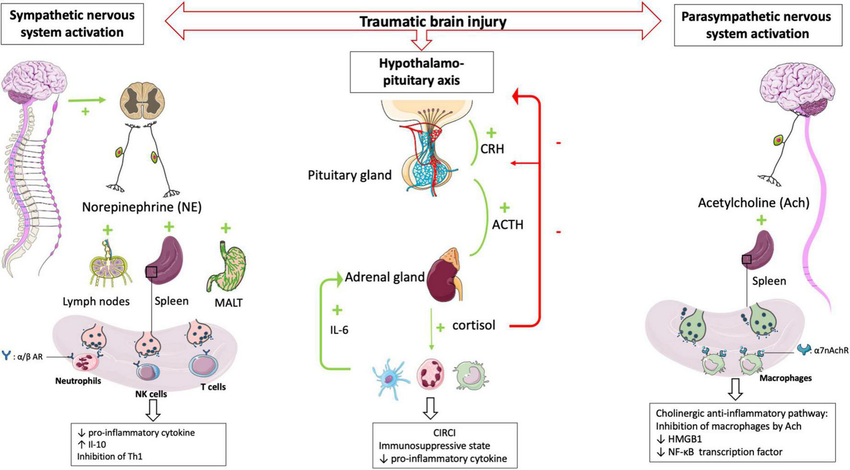
- Autonomic nervous system: This network of nerves directly innervates lymphoid organs, influencing immune cell activity through neurotransmitters.
- Cytokines and chemokines: These signaling molecules, produced by both immune and nervous system cells, coordinate responses across both systems.
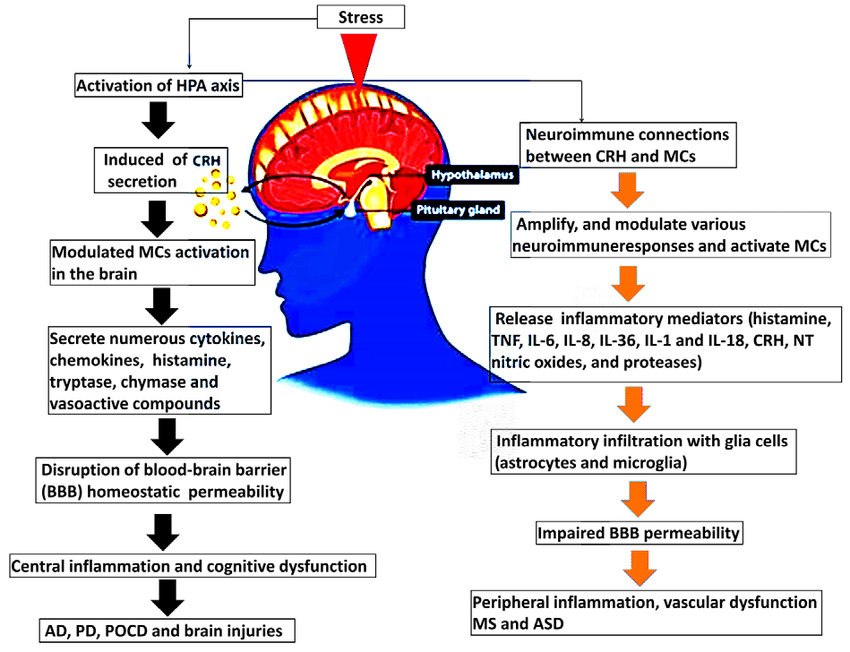
- Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis: This neuroendocrine pathway regulates stress response and can modulate immune function through hormones.
Immune Dysfunction and Neurological Disorders
Disruptions in the delicate balance between the immune and nervous systems can contribute to various neurological disorders:
- Autoimmune diseases: In conditions like multiple sclerosis, the immune system mistakenly attacks components of the CNS, leading to damage and neurological deficits.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Chronic inflammation, potentially driven by a dysregulated immune response, is implicated in the progression of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
Research is ongoing to better understand the immune system's role in neurological disorders. Maxanim (Gentaur Group) is a company supplying resources for this research. Click here for more info.
Future Directions
Understanding the intricate interplay between immunity and the nervous system holds promise for new therapeutic approaches. By deciphering the communication pathways, researchers aim to develop targeted interventions for neurological disorders and more effectively modulate immune responses.
Explore how the nervous system may influence the immune system in this video.
Immunity and the Nervous System: A Collaborative Network