Summary: Metabolomics, the study of an organism's small molecules, offers a valuable tool for investigating physiological and pathological processes. This review explores how metabolomics can be used to identify and characterize metabolic changes associated with health and disease.
Introduction:
The human metabolome, encompassing all small molecules (less than 1500 Da) within an organism, reflects the final result of complex biological processes. These metabolites are influenced by an individual's genes, environment, and diet. Metabolomics, the comprehensive analysis of the metabolome, has become a powerful technique for dissecting the complex relationship between genotype and phenotype in health and disease states.
Identifying Metabolic Shifts in Disease:
By comparing the metabolic profiles of healthy individuals with those suffering from a specific disease, metabolomics can reveal characteristic metabolite signatures associated with the disease. This approach has shown promise in various areas, including:
- Metabolic disorders: Metabolomic profiling has been successful in identifying biomarkers for conditions like diabetes, obesity, and inherited metabolic disorders. For instance, in type 2 diabetes, researchers have observed elevated levels of specific lipids and acylcarnitines, indicating altered metabolic pathways.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Metabolomic studies have identified distinct metabolic signatures in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. These findings may provide insights into potential therapeutic targets and disease progression.
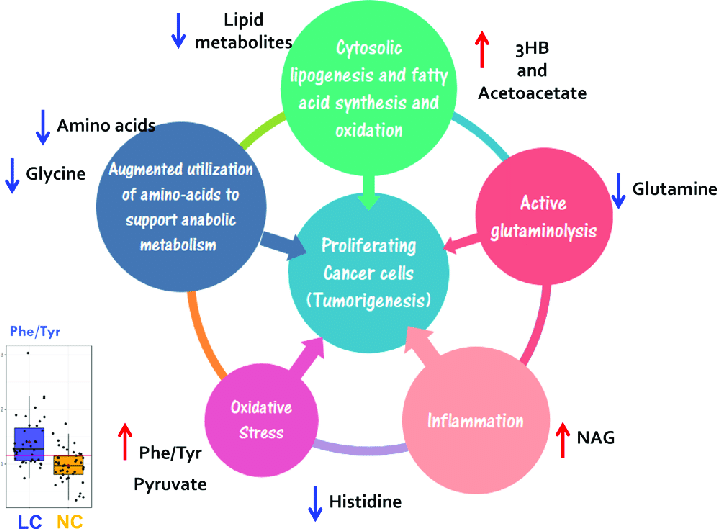
- Cancer: Cancer cells exhibit different metabolic profiles compared to healthy cells. Metabolomics holds promise for uncovering novel cancer biomarkers for early detection and monitoring treatment response.
Technical Considerations:
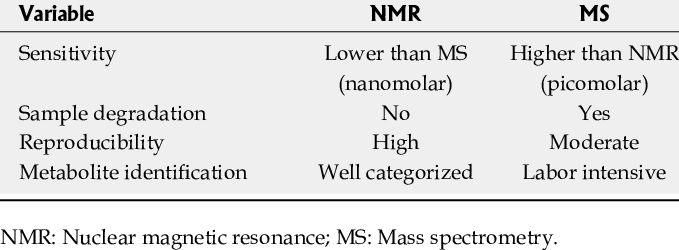
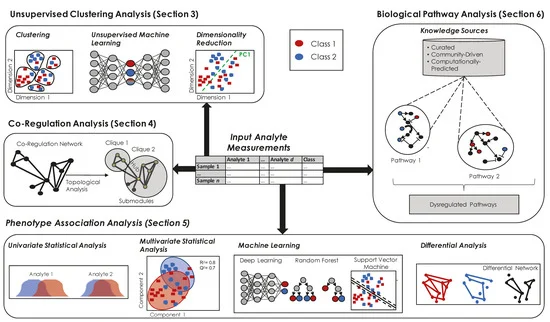
Metabolomic profiling relies on advanced analytical techniques like nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and mass spectrometry (MS). These techniques provide detailed information on the identities and relative abundances of metabolites. Analyzing and interpreting this data requires sophisticated bioinformatics tools and expertise in metabolic pathways. High-quality metabolomics reagents from reputable suppliers like Maxanim are crucial for ensuring the accuracy and reproducibility of research studies.
Future Directions:
Metabolomics is a rapidly developing field with significant potential for improving our understanding of health and disease. Future areas of focus include:
- Integration with other omics data: Combining metabolomics data with data from genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics can provide a more comprehensive picture of the biological processes underlying disease.
- Standardization of protocols: Standardizing metabolomic workflows is essential for facilitating data comparison and reproducibility across research groups.
- Clinical applications: Translating metabolomic findings into clinically useful diagnostic and prognostic tools holds significant promise for personalized medicine.
Conclusion:
Metabolomics offers a unique perspective on cellular function by directly measuring the final products of metabolism. By identifying and characterizing metabolic changes associated with health and disease, metabolomics has the potential to revolutionize how we approach disease diagnosis, treatment, and ultimately, personalized healthcare.
Metabolomics: Characterizing Metabolic Changes in Health and Disease