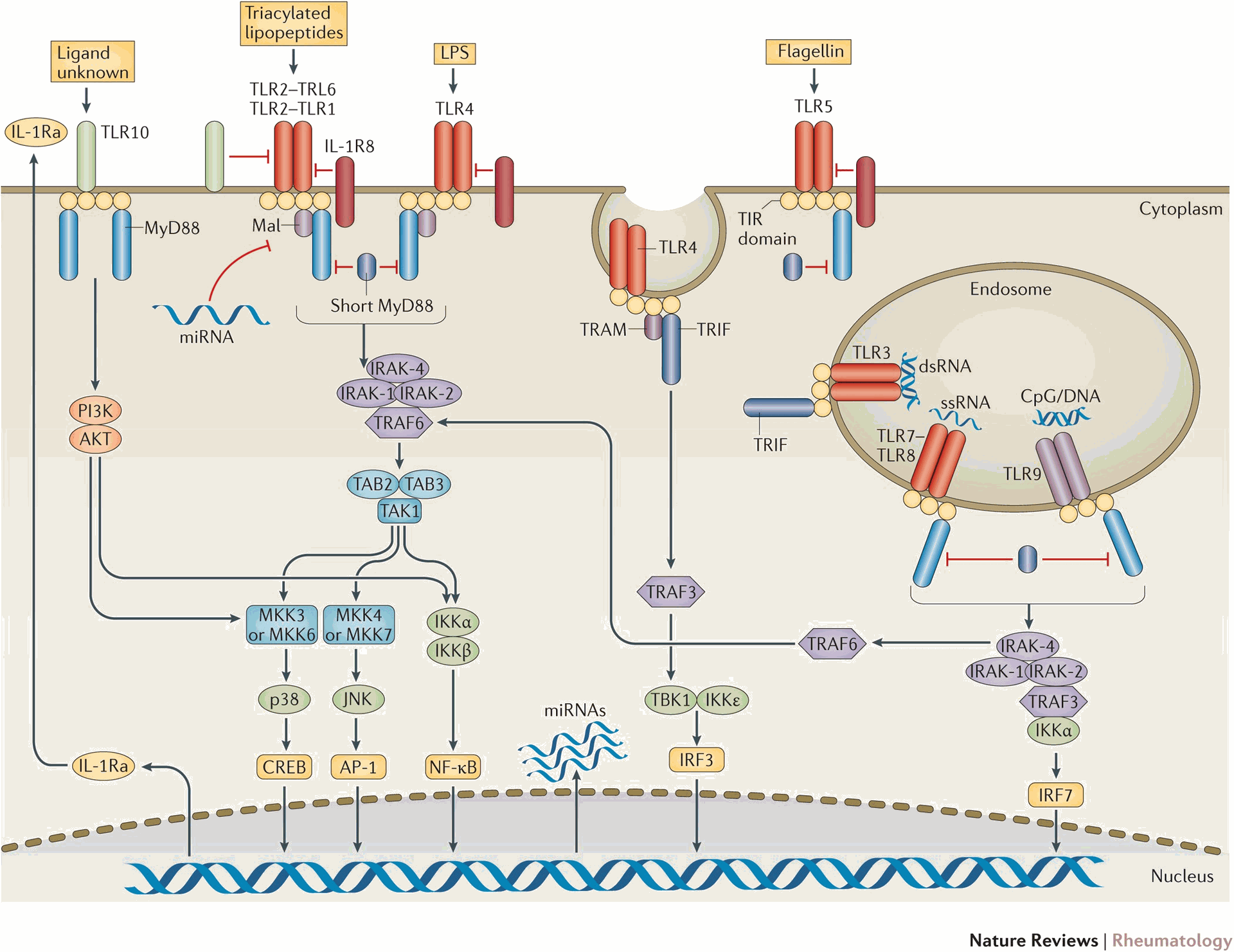
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are essential molecules in the immune system, recognizing invaders like bacteria and viruses. Recent research reveals a more intricate role for TLRs in autoimmune diseases.
TLRs and Self-Tolerance:
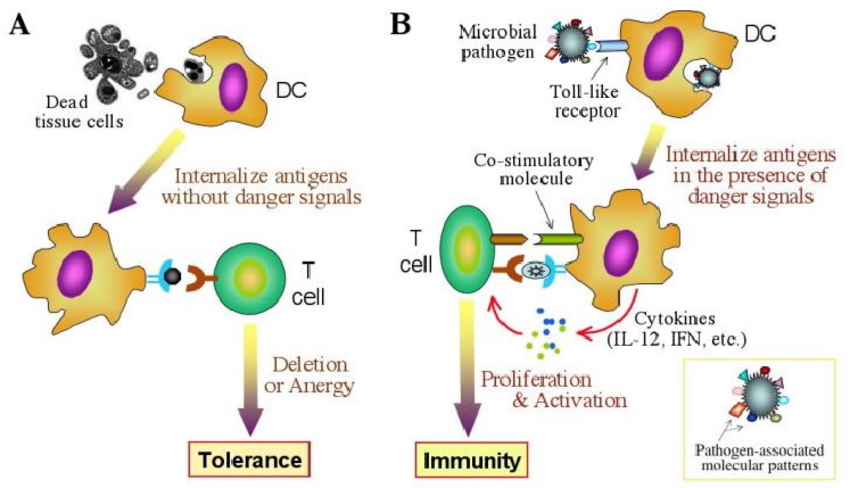
Normally, TLRs help maintain self-tolerance, preventing the immune system from attacking the body. This is achieved through several mechanisms:
- T cell silencing: TLR activation can inactivate T cells that might target healthy tissues.
- Regulatory T cells: TLRs can promote the development and function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) that suppress immune responses to the body's own tissues.
- Immune ignorance: TLR signaling can contribute to hiding self-antigens from the immune system, preventing a mistaken immune response.
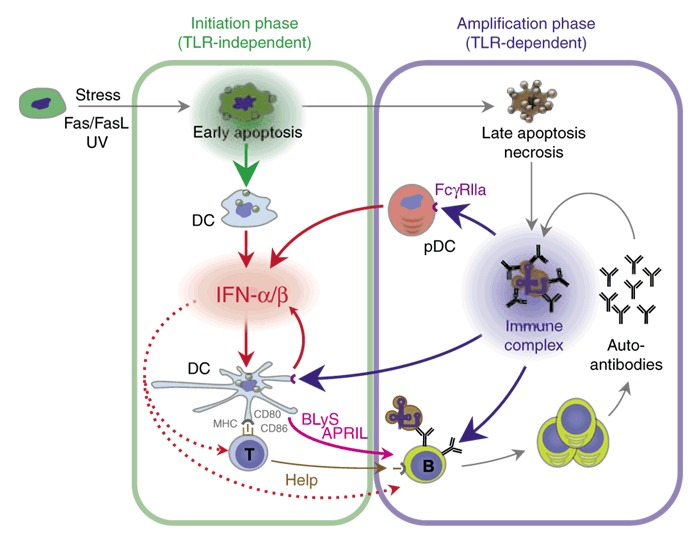
TLR Dysregulation and Autoimmunity:
However, problems with TLR signaling can lead to autoimmunity:
- Excessive inflammation: Uncontrolled TLR activation by the body's own molecules can trigger chronic inflammation, a feature of many autoimmune diseases.
- Mistaken identity: Microbial molecules can resemble the body's own molecules. TLRs targeting these mimics can mistakenly attack healthy tissues.
- Tolerance loss: Issues with TLR signaling can impair the mechanisms mentioned above, leading to T cell attacks on healthy tissues and Treg dysfunction.
Examples of TLRs and Autoimmunity:
- TLR2 and TLR4: Linked to rheumatoid arthritis, where they may be activated by self-antigens in joints, causing inflammation.
- TLR7 and TLR9: Involved in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), where they might recognize the body's own nucleic acids and trigger autoimmunity.
- TLR3: Emerging evidence suggests its role in Sjögren's syndrome, an autoimmune disease affecting glands.
If you are working in this research field, all the components can be supplied by Gentaur Group (Maxanim).
Treatment Implications:
Understanding TLRs in autoimmunity opens doors for potential treatments:
- TLR modulators: Specific drugs could activate Tregs to promote tolerance or block excessive inflammatory responses.
- Targeting TLR pathways: Drugs targeting molecules downstream of TLR signaling are being explored for managing autoimmune diseases.
Conclusion:
TLRs play a complex role in both defending against infections and maintaining self-tolerance. When TLR signaling goes awry, it can contribute to autoimmune diseases. Research into TLR pathways holds promise for developing new therapies to regulate immune responses and restore tolerance in autoimmune conditions.
Learn more about Toll-Like Receptors in this video:
TLRs in Autoimmune Diseases: Complex Role, Potential Target